Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Please send an email to [email protected] for any questions.
An object is a self-contained unit that combines data (attributes/properties) and behavior (methods/functions). Objects are created from classes, which act as blueprints.
In object-oriented programming (OOP), an object is a self-contained unit that combines data (attributes/properties) and behavior (methods/functions). Objects are created from classes, which act as blueprints.
Chào mừng đến vói trang danh sách các thuật ngữ của sản phẩm Jframework.io.
A license in software is a legal agreement that specifies how a user can use a particular software product. It defines the rights, restrictions, and responsibilities of the software provider (developer, company) and the end user (individual, organization).
In JFW, it means a Subscription license.
See URL
See Jframework
Jframework is an adaptable authentication and authorization platform designed to enhance the security and user experience of your applications' login systems. It offers a range of features, including fine-grained authorization, universal login, single sign-on (SSO), multifactor authentication (MFA), and passwordless authentication. These capabilities enable developers to implement robust identity management solutions across various technology stacks.
A brand is the identity and perception of a company, product, or service in customers' minds. It includes a unique combination of name, logo, design, values, messaging, and customer experience that differentiates a business from competitors.
A Brand Owner is an individual or company legally owning and controlling a brand, its trademarks, and intellectual property. The brand owner has the exclusive rights to use the brand name, logo, and associated assets for business purposes.
Built-in objects have been built (built-in) in the JFW system, such as Permission and Roles (called built-in permission and built-in role). For example, when creating a brand, there will be a list of available permissions or roles such as Owner, Admin, Editor, and Viewer.
Trong tài liệu này có dùng 1 số thuật ngữ và đôi khi vẫn để là tiếng Anh (không dịch qua tiếng Việt), hoặc 1 số từ viết tắt.
DB
Database
MFA
Multi-Factor Authentication
GUID
Globally Unique Identifier
SMS
Short Message Service
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
URL
Uniform Resource Locator
JFW
Jframework
Entry
In programming, "entry" can refer to different concepts, depending on the context.
"End-Dev" is not commonly used as a standard industry term in software development. However, based on its structure, it could be interpreted in a few possible ways:
An end-user is the person who ultimately uses a product, system, or software after it has been developed, distributed, or deployed. They interact with the software or hardware for its intended purpose without necessarily knowing the technical details behind its creation.
An event in programming is an action or occurrence that a system detects and responds to. Events are commonly used in event-driven programming, where the flow of a program is determined by these occurrences instead of a pre-defined sequence.
Some words are confusing and difficult to understand (because they are translated from English), so it may be necessary to specify and choose an equivalent word. The current color for the document is bold.
Event Type
Example
Where It’s Used
User Interaction Events
Click, key press, mouse movement
Web apps, GUIs
System Events
Startup, shutdown, error messages
Operating systems, servers
Network Events
Request received, connection lost
Web servers, APIs
Hardware Events
USB connected, low battery
Embedded systems, mobile devices
Custom Events
Business logic events (order placed, payment processed)
Enterprise applications
Template, Pattern
URL, Domain, Link
URL, Webhook, URL_Listener, URL_IPN, Payload
Provider, Partner
Ticket, Issue, Helpdesk, Help-desk, Community
Link, Register, Attach, Create, New, Add
Delivery, Send
permission, right, priviledge
Mockup, mock-up
Mock test, mock-test
Usecase, use-case, user case
Notation, term, glossary, vocab
Redeem, claim
Brand constant, App Constant
System, App
Tracking, Log
Billing vs Payment vs Price
Description, Public_Notes, Private_Notes, Internal_Notes, Notes.
Local database, internal database, temporary database, client database, and device database.
trên thiết bị (device) có lưu file database tạm nhu sqlite, ...
*
In the context of currency exchange, the term "Rate" refers to the exchange rate, which is the value of one currency in relation to another. It tells you how much one unit of a currency is worth in another currency.
See the Exchange rate.
"Redeem" means to exchange, claim, or convert something of value, such as points, vouchers, or credits, for a reward, cash, or service.
See the Referral User
A Referral User is a person who joins a service, buys a product, or signs up for an account through a referral link or referral program. This user is typically introduced by an existing customer who gets rewarded for the referral.
A Referral Code is a unique alphanumeric code assigned to users that allows them to refer others to a service, product, or platform. When a new user signs up or purchases using the referral code, the referrer and the new user may receive rewards like discounts, credits, or cashback.
A Referee is someone who is being referred to a service, job, or opportunity by another person.
A Reseller is a person or business that buys products or services from a manufacturer, wholesaler, or provider and then sells them to customers for a profit. Resellers do not typically produce the goods themselves but act as intermediaries.
See the Distributor.
A resource can be used to accomplish a task, support a process, or achieve a goal. Resources can be physical, digital, financial, or human. Here is in JFW:
Object
Service
Xem Role-Base Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security model that restricts access to systems, data, or resources based on a user's role within an organization. Instead of granting permissions to individual users, permissions are assigned to roles, and users are then assigned to those roles.
A role is a defined set of permissions, responsibilities, or actions assigned to a user or system within an organization or application. Roles help control access by grouping users with similar privileges.
A group of related features offered together.
Password salt is a random data string added to a password before hashing to improve security. It helps protect against rainbow table attacks and makes it harder for attackers to crack passwords using precomputed hashes.
Pay-as-you-go (PAYG) is a pricing model where users pay only for what they use instead of a fixed monthly or annual fee. This model is commonly used in cloud computing, utilities, and mobile services.
A pattern is a repeated or structured arrangement of elements, concepts, or behaviors used in various fields, such as programming, design, mathematics, and problem-solving.
See #Template
Pattern vs Template is different.
Payment transfers money or value from one party to another to transfer goods, services, or financial obligations. Payments can be made using cash, digital transactions, bank instruments, or other financial instruments.
A Payment Gateway is a secure service that authorizes and processes online business payments. It acts as a bridge between customers, merchants, and banks to ensure the safety and success of transactions.
In the Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) model, permissions define the specific actions a user can or cannot perform. These permissions are assigned to roles, and users are granted access based on their roles.
Price refers to the money a customer must pay to purchase a product or service. The software industry's pricing models vary based on business strategy, customer needs, and market conditions.
A website protocol refers to the rules governing how data is transmitted between a web server and a browser (or client). It ensures secure, efficient, and structured communication over the internet.
See the Protocol.
An invoice is a document issued by a seller to a buyer that details a transaction, specifying the goods or services provided, their quantities, prices, payment terms, and due dates. It serves as a formal request for payment and is commonly used in business and accounting.
In help desk support, an issue refers to a problem, request, or concern reported by a user that requires assistance from the support team. It can be related to software, hardware, network, or user account problems.
A device is a physical or virtual machine designed to perform a specific function, often involving data processing, communication, or control. Devices can range from hardware components like computers and smartphones to virtual or software-based devices in cloud computing.
A software distributor is a company or individual that buys software licenses from developers or vendors and resells them to businesses, resellers, or end users. They act as intermediaries between software vendors and customers, handling sales, support, and sometimes value-added services.
Xem Scheduler
A scheduler in software is a system component that manages and controls the execution of tasks, processes, or jobs based on predefined rules and timing. It determines which task runs, when it runs, and for how long.
Scope refers to the boundaries or limits within which something is defined, accessed, or applicable. It is widely used in software development, project management, and security.
Soft deletion is a technique used in databases and applications in which data is not permanently deleted but marked as "inactive" or "deleted." This allows for data recovery and maintains historical records.
In software, a service is a self-contained unit of functionality that performs specific tasks and can run independently or as part of a more extensive system. Services are commonly used in operating systems, web applications, cloud computing, and microservices architectures.
JFW supports 11 services, such as Identity, CDN, Security, Billing, Payment, ...
In project management, a statement refers to a formal document or declaration that defines key aspects of a project, such as its objectives, scope, deliverables, constraints, and assumptions. Statements help set clear expectations and guide project execution.
In software and business, a subscription is a pricing model in which users pay a recurring fee (monthly, yearly, or for a custom period) to access a product or service.
A Subscription Type defines the duration and conditions of access to a service or product. For example, a 90-day subscription allows users to access the service for 90 days from the activation date, after which they must renew or extend it.
It is JFW or service, an object without a specified Brand.
Category
Examples
Purpose
Computing Devices
Laptop, Desktop, Server
Process data and run applications
Mobile Devices
Smartphone, Tablet, Smartwatch
Portable computing and communication
Networking Devices
Router, Switch, Modem
Connect and transfer data over networks
Storage Devices
SSD, HDD, USB Drive
Store and retrieve data
IoT Devices
Smart Home Devices, Wearable Tech
Internet-connected automation and monitoring
Input Devices
Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner
Send data to a computer
Output Devices
Monitor, Printer, Speaker
Display or output processed information
Cloud & Virtual Devices
Virtual Machine (VM), Cloud Server
Software-defined computing environments
Role
Function
License Management
Distributes software licenses to resellers or businesses
Sales & Marketing
Promotes software solutions in target markets
Technical Support
Provides troubleshooting and customer support
Customization & Integration
Offers value-added services like software customization
Training & Education
Provides training on software usage
Compliance & Legal Support
Ensures licenses comply with regulations
Type
Description
Example
Retail Software Distributor
Sells software directly to end users or businesses
Microsoft Office distributors for small businesses
Value-Added Distributor (VAD)
Offers extra services like support, training, and customization
A cybersecurity distributor offering setup & consulting
Cloud Software Distributor
Focuses on SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solutions
AWS or Microsoft Azure resellers
OEM Software Distributor
Bundles software with hardware products
Windows pre-installed on Dell laptops
Enterprise Software Distributor
Supplies large-scale software solutions to businesses
ERP software distributors (SAP, Oracle)
Feature
Software Distributor
Software Reseller
Buys From
Software vendors/developers
Distributors or vendors
Sells To
Resellers, businesses, or end users
End users or businesses
Stock Management
Manages software inventory and licenses
Usually sells on-demand
Additional Services
Provides support, training, and consulting
Focuses mainly on sales
Example
Distributes Microsoft 365 licenses to IT resellers
An IT company selling Microsoft 365 to its clients
Feature
Soft-Delete
Hard-Delete
Data Recovery
✅ Possible
❌ Not possible
Performance Impact
🚨 Can slow queries (more filtering)
⚡ Faster deletion
Storage Usage
📈 More space required
✅ Less space used
Audit & History
✅ Retains history
❌ No record remains
sqlCopyEditUPDATE users
SET is_deleted = TRUE
WHERE user_id = 123;sqlCopyEditUPDATE users
SET is_deleted = FALSE
WHERE user_id = 123;See Content Delivery Network
A CDN is a distributed server system that delivers web content (images, videos, scripts, HTML, etc.) quickly and efficiently to users based on their geographical location.
CDNs help reduce latency, improve website performance, and enhance security by caching content closer to end users.
A coupon is a promotional tool that offers a discount, special offer, or other benefits to users when they purchase a product or service. In the software industry, coupons are commonly used to attract new customers, retain existing ones, and boost sales.
In sales, a Claim refers to a statement, promise, or assurance made by a business or salesperson about a product, service, or offer. It is used to convince potential customers by highlighting benefits, features, or guarantees.
See Conf
Động từ, dịch là cấu hình. Đôi khi dùng trong use-case hay câu: "configre the settings".
Configuration refers to setting up, customizing, and adjusting the components of a system, software, hardware, or network to function according to specific requirements. It involves defining settings, parameters, and preferences to ensure optimal performance.
A concept is an abstract idea, thought, or principle that helps explain or define something. It is a foundation for understanding, reasoning, and problem-solving in various fields such as business, science, philosophy, and technology.
A constant is a fixed value that does not change throughout the execution of a program, a mathematical equation, or a scientific principle. It is widely used in programming, mathematics, and physics.
A commission is a payment or fee earned based on a percentage of sales, transactions, or services provided. It is commonly used in sales, business, finance, and freelance work as an incentive for performance.
🔹 Types of Commission
Type
Definition
Example
Sales Commission
Paid based on the number or value of sales made
A real estate agent earns 3% of a home sale price
Performance-Based Commission
Earned when specific targets or goals are met
A salesperson gets a $500 bonus for exceeding quota
Flat-Rate Commission
A fixed amount paid per transaction
A recruiter gets $1,000 per hired candidate
Tiered Commission
Increases as sales volume grows
5% for the first $10,000 in sales, then 10% beyond that
Residual Commission
Ongoing payments for recurring sales
Insurance agents earn commissions on policy renewals
Affiliate Commission
Earned for referring customers to a business
Bloggers get a 10% commission from product referrals
🔹 Commission in Business & Sales🔹 Used as an Incentive – Motivates employees and salespeople to perform better. 🔹 Encourages Productivity – Higher sales lead to higher earnings. 🔹 Common in Affiliate Marketing – Online influencers earn commissions from referrals.
📌 Example in Sales:
A salesperson sells a $50,000 car with a 5% commission rate.
Their commission = $50,000 × 5% = $2,500.
cPanel is a web-based control panel allowing users to manage web hosting services easily. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing domains, files, databases, emails, security, and more without needing advanced technical skills.
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete—the four fundamental operations used to manage objects in databases, APIs, and applications.
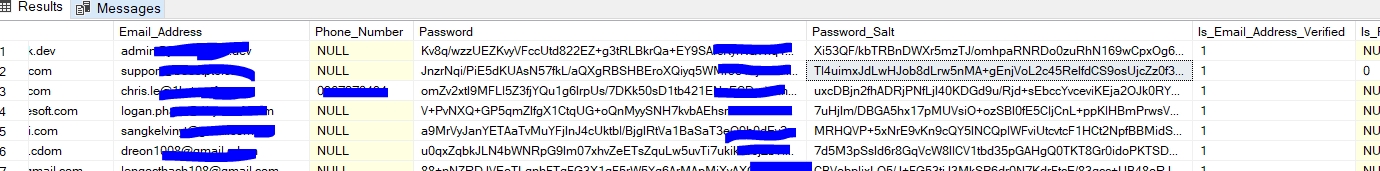
Admintool (Admin Tool hoặc AdminTool) là thuật ngữ viết tắt của "administration tool". Trong JFW, Admin Tool là công cụ quản trị được xây dựng trên JFW.
Administrator (viết tắt: Admin) có nghĩa là quản trị viên, người chịu trách nhiệm quản lý và giám sát một hệ thống, tổ chức hoặc nền tảng cụ thể.
API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols allowing different software applications to communicate. APIs enable data exchange, service requests, and automation between systems without requiring direct access to their internal code
An API Protocol is a set of rules and standards that define how APIs send and receive data between systems. It ensures that different applications can communicate smoothly, securely, and efficiently over networks (like the internet).
For example, protocol.jframework.io is an API protocol in JFW. Of course, "[protocol]" must be replaced for SSL and secuirty like https://ajdkhf2323khlasd.jframework.io.
Auth0 is an Identity and Access Management (IAM) platform that provides application authentication and authorization services. It helps developers secure user logins, manage user identities, and enforce access control without building authentication from scratch.
🔹 Owned by Okta (since 2021) 🔹 Common Uses: Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), API security 🔹 Supports: Web apps, mobile apps, APIs, IoT
